Welcome, ladies! Today, we're diving deep into a common obstacle many women face on their weight loss journey: being under muscled. You might be diligent with your diet, logging hours on the treadmill, yet still struggle to shed those stubborn pounds. Here's the scoop: it's time to shift our focus from just losing weight to building muscle. Let's explore why your muscle mass matters and how it impacts your weight loss goals. Understanding the Problem: So, what exactly does it mean to be "under muscled"? In simple terms, it's having inadequate muscle mass relative to your body composition. As we age, especially between the ages of 30-50, our muscle mass naturally declines due to factors like hormonal changes, decreased activity levels, and even dietary habits. This decline in muscle mass not only affects our strength and mobility but also plays a crucial role in our ability to lose weight effectively. The Muscle-Fat Connection: Here's the kicker: muscle is a metabolically active tissue, meaning it burns calories even at rest. The more muscle mass you have, the higher your basal metabolic rate (BMR), which translates to more calories burned throughout the day. On the flip side, excess fat tissue does little in terms of calorie expenditure. So, if you're carrying more fat than muscle, your body becomes less efficient at burning calories, making weight loss an uphill battle. The Benefits of Building Muscle: 1. Increased Metabolism: By building muscle through resistance training, you can rev up your metabolism, making it easier to create the calorie deficit necessary for weight loss. 2. Improved Body Composition: Building muscle while losing fat leads to a leaner, more toned physique, rather than simply becoming smaller in size. 3. Enhanced Strength and Functionality: Strong muscles not only support you during workouts but also in daily activities, promoting better posture, balance, and overall vitality. How to Build Muscle and Lose Weight: 1. Strength Training: Incorporate resistance training exercises into your routine at least 2-3 times per week. Focus on compound movements like squats, deadlifts, lunges, and rows to target multiple muscle groups simultaneously. 2. Progressive Overload: Continuously challenge your muscles by gradually increasing the weight, reps, or intensity of your workouts over time. This stimulates muscle growth and prevents plateaus. 3. Balanced Nutrition: Ensure you're consuming enough protein to support muscle repair and growth, while also maintaining a slight calorie deficit to facilitate fat loss. Opt for nutrient-dense foods like lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. 4. Rest and Recovery: Don't overlook the importance of rest days and quality sleep. Muscles need time to repair and grow, so prioritize recovery to avoid burnout and injury. Conclusion: Ladies, if you've been struggling to lose weight despite your best efforts, it's time to shift your focus to building muscle. Remember, it's not just about the number on the scale, but rather achieving a healthy balance of muscle and fat for long-term success. By incorporating strength training into your routine and prioritizing muscle growth, you'll not only transform your physique but also supercharge your metabolism and reclaim your confidence. Here's to becoming strong, empowered women who can conquer any challenge that comes our way! So, are you ready to say goodbye to being under muscled and hello to a stronger, leaner you? Let's do this together! Coach Kayli
0 Comments
Blog Post By Kayli Montoya-HustonNASM Certified Personal Trainer & NCI Certified Nutrition Coach L1 and Mindset Coach Embarking on a weight loss journey can be challenging, especially when you're committed to shedding those stubborn pounds but see minimal results. If you're wondering why your body fat isn't budging, you're not alone. In this blog post, we'll explore the top 10 reasons that might be hindering your fat loss progress and provide practical solutions to overcome these obstacles.
Inadequate Caloric Deficit:
Conclusion: Identifying and addressing these roadblocks can pave the way for successful fat loss. Remember, patience and consistency are key. Consult with a qualified nutrition coach or personal trainer to personalize your approach and maximize your results. Your fitness journey is unique, and understanding these reasons can help you overcome obstacles and achieve your body fat loss goals. Welcome to 2024!
As we dive into the new year, let's focus on what really matters for fat-loss. I'm not about quick fixes or fads. It's all about practical steps you can actually stick to. This is my 9th January working in fitness, and I'm often inspired and rejuvenated by the new year too. Many people bash "resolutions," making it feel vulnerable to admit having big health goals for the new year. But you aren't alone. There are plenty of others watching this who want to improve how they look, move, and feel. The number one thing I hear from people at the beginning of each new year is their desire to lose weight, closely followed by wishes to eat "better" and "exercise more." Let’s tackle two out of these three: losing weight and eating better. These are the two things (besides maybe better sleep) that will help you feel better. So here is Tip #1 of the 10 no-nonsense strategies to help you lose fat more easily this year.
Stay strong, Coach Kayli! Here's what everyone gets wrong about losing fat quickly... You might have two pre-conceived notions when you hear words like "rapid fat loss."
For the first notion, I get it. The media sucks in almost all ways. For the second notion, I think that's generally sound advice ⏤ it's advice I give all the time. But that doesn't mean there's not a right way to lose fat, fast. If you do it correctly, it can be an excellent way to kickstart your fat loss and ramp up motivation from quick results. I've seen it work time and time again with my 1:1 fat loss clients, along with the other 50+ people who've gone through the Fat Loss Accelerator Phase of my program in the past. The key, however, is to avoid these critical mistakes. 7 Rapid Fat Loss Mistakes (& How To Avoid Them) Mistake #1: You don't do an honest self-audit.
Mistake #2: You mindlessly cut too many calories too quickly. How many calories you take away and where those calories come from are what separates successful rapid fat loss from straight-up "crash-dieting." When your approach is to simply eat way less and move a lot more, it's a recipe to ramp up cravings, lose muscle and strength, and slow your metabolism too quickly. You need a "smart" calorie deficit and just enough of the right cardio to lose pure body fat, fast, without "crashing" your metabolic rate. Mistake #3: Focusing on losing weight, instead of fat. Traditional diets focus on total weight loss with no regard to the composition of those pounds lost. Losing 5 lbs sounds great! But what if it was 2 lbs of fat and 3 lbs of muscle? And what if you could improve that ratio to 4.5 lbs of pure fat and only 0.5 lb of muscle? That should be the goal, assuming you want to actually LOOK noticeably leaner, more muscular, and defined. (Not just see an arbitrary number on the scale go down.) How you do that is by avoiding these next two mistakes. Mistake #4: Not eating enough protein. This piggy-backs off the last two points. Eating a higher-protein diet, especially when in a large calorie deficit, is crucial for retaining muscle mass AND keeping those cravings away. You probably know protein builds muscle, but lesser known is that protein is the most satiating macronutrient (more than carbs and fats). So it's great for staying fuller, longer. Aka, you don't feel like you're starving every day, and you can stick to your diet much easier. Mistake #5: Not having a smart strength training plan to work synergistically with rapid fat loss. To avoid having the "skinny-fat" and "deflated" look from losing weight quickly, you have to take your workouts seriously. A smart program for rapid fat loss is designed to 1) retain/build as much muscle and strength as possible and 2) maximize recovery and minimize fatigue. You want to use your diet to lose fat and your strength workouts to retain muscle, which is exactly how I designed the Accelerator Diet Phase and Accelerator Workouts. Mistake #6: Not having education, support, and professional guidance to guide you to the finish line. Rapid fat loss is not for the weak-hearted, nor something to take lightly. It's even harder to go at it alone. The best approach is to use rapid fat loss to "jumpstart" your long-term weight loss journey and NOT as a sustainable, long-term approach. Use it to build healthier habits and learn new skills to use once the rapid fat loss period is over. Ideally, with a coach or expert guiding you every step of the way. Which brings me to the last, and possibly most important point. Mistake #7: Not having a plan to transition out of the rapid fat loss period without rebounding. Rapid fat loss is pointless if you just end up gaining all the weight back. Which, if done incorrectly, you're prone to gain back even more than traditional diets. This isn't to scare you, because it's not irreversible and you won't "damage" your metabolism, but it's the truth. A slower, calculated transition is key. (Again, hopefully with someone who knows their stuff.) As you could've guessed, this is the part where I pitch my Phoenix Rising Method as the solution ⏤ and, you're right. I created the Rise Method which includes the (Fat Loss Accelerator) Phase with every one of these mistakes in mind so you can safely lose lots of fat, fast. If you've decided you want to learn more, you can apply here for a free discovery call. - Coach Kayli Have you ever been told the reason you’re not losing weight is because “you’re eating too little”.
If so, I am also sure you have been told your body has gone into “starvation mode”. Where people tend to explain it, as your body is holding onto all your body fat because you haven’t been eating enough calories. Spoiler Alert: I’m here to explain to you why this is in fact a myth. As everything you hear in the fitness and health industry there is a sliver of truth behind this statement. In fact, I myself am guilty of using this phrase in the past. Thankfully I have continued to learn and research the science of our metabolism. Next let's break down the common definition of “starvation mode”. What is Starvation Mode? Starvation mode is not a scientific term. It is a popular phrase used to imply that when you cut calories too low, your body goes into a protection mode, slowing your metabolism and calorie output so that you stop losing weight. This concept is rooted in your body's survival mechanisms. If you ever found yourself without food for long periods of time, it would not be beneficial for your body to continue to burn calories at a normal rate; instead, your metabolism would shift to preserve as much energy as possible to prolong your life. But starving to death is not quite the same thing as dieting and you will still lose weight in the process of wasting away without food. How Long Can You Survive Without Food? With access to water and electrolytes, your body can survive for quite some time without food, depending on the person and how much body fat you have. Some research suggests that you can go more than a month without food. And in some religions, long fasts are commonly practiced with potential health benefits. Starvation mode is not a real term, but metabolic adaption is, and it’s a known phenomenon. How drastically it affects your weight loss progress is another story. Your body can compensate for decreased calories by slowing your metabolism down as much as 30% through adaptive thermogenesis. But the effects of adaptive thermogenesis are typically short-lived, and for most the difference could be as little as a 5% decrease in basal metabolic rate (BMR), and it does not indicate a damaged metabolism. So what is the verdict? In all of the studies referenced to support starvation mode, weight loss was a factor. And it is crucial to note that any weight loss can cause you to have a lower BMR - since it just takes less energy to move around a smaller object. Why You're Not Losing Weight and How to Fix it If you find that you’ve hit a weight loss plateau, it does not mean you are in starvation mode. Some more common factors are likely at play, including the following: You're Not Tracking Your Food Intake It's pretty impossible to know if you are in a calorie deficit if you aren't tracking your food intake. Before assuming something else is at play, keeping an accurate food diary is the best place to start. Even if you've been tracking, take a look at how diligent you are being with this habit.
You can also use your tracking app to get weekly calorie and macro averages - this is the best way to see how well you’ve stuck to your diet consistently, as well as where you could use some work. You're Not Eating the Right Amount of Calories Typically, if you aren't losing weight, you are eating more calories than you think. Or if you've recently lost weight, you likely have a new maintenance calorie amount and may need to eat fewer calories to continue losing. This is why many popular weight loss plans will use a phased approach to cutting, helping you to stay in a calorie deficit and continue losing weight with incremental calorie cuts. Start by figuring out how many calories you need to eat a day to maintain your current weight and then calculate your new weight loss calorie needs from that starting point. You're Always on a Diet It might also just be that your body needs a break. If you've been dieting for more than a few months, it might be time to give your body time to adjust to your maintenance calorie level. Jumping from one diet to the next and constantly trying to cut calories can do more harm than good. It is much easier to stick to a diet and continue to get results if you understand how to maintain results in the first place. Been on a really low-calorie diet for a while and scared to add calories back in? Try upping your intake a few hundred calories a week to start, until you reach your maintenance level. And then stick to your maintenance for at least a month to give your time to adjust and reset your metabolism. You're Too Focused on the Scale Oftentimes dieters are focused solely on fat loss, but their total body composition is crucial to getting better results and making them stick. Not to mention, if you are cutting calories too low for too long, you’re at risk of losing precious calorie burning tissue - your muscle. Gaining muscle is essentially the opposite of “starvation mode”. Your muscle mass is the biggest determinant of your metabolic rate, and the more you have, the more you can eat and maintain your weight. Plus, muscle is the tissue behind that lean, toned look most of us are striving to achieve in the first place. While muscle growth is typically achieved through weight gain, which would ultimately increase your metabolism even further, it is possible for some people to build muscle in a calorie deficit. But at the very least, you should be focused on protecting your muscle while dieting. To keep your lean mass intact while dieting, be sure to incorporate the following:
What are the Minimum Calories for Weight Loss? While starvation mode may not technically exist, starving yourself to lose weight is still not recommended. A very low-calorie diet may work at first, but it’s likely not going to do you favors in the long run. It can be dangerous for some people, lead to disordered eating habits, and does not typically lead to sustainable results, since most people do not change bad habits once they resume eating again. In addition, extreme dieting is impossible to maintain, causing painful hunger cues, irritability, mood swings, decreased energy, poor concentration, and sucks your willpower dry, all of which makes sticking to a diet that much harder. Instead, stick to a more attainable approach to dieting with no more than a 15-20% decrease from your estimated daily energy needs. Slow and steady weight loss of 0.5 to 1% body weight per week is much easier to keep off and you will be much happier and more successful with a more measured and sustainable diet plan approach. Need help figuring out how many calories you need each day? I’d be happy to help you figure out your starting numbers. Simply click the button below and fill out this short form explaining your goals and I’ll reach within 24hrs! Blog Post by Coach JulieNCI Certified Nutrition Coach L1 & Certified Mindset Coach  Wegovy and Ozempic are both GLP-1 (glucagon like peptide). With GLP-1 drugs, you will lose muscle mass if you are not doing some sort of resistance training. “Much of the "weight loss" resulting from GLP-1 agonists is the loss of muscle, bone mass, and other lean tissue rather than body fat (Ida, et al.).” When taking GLP-1 drugs it’s important to focus on getting adequate protein to at least maintain muscle mass. (Usually .75g of protein per pound of lean body mass is adequate. If your goal weight is 150 pounds that means 113g of protein per day.) A significant loss of bone mass, for example, predisposes serious bone diseases such as osteopenia and osteoporosis. And a significant loss of muscle mass lowers metabolic rate (increasing the risk of weight regain), raises the risk of falls, and impairs function and quality of life. Research has found that when people stop taking Wegovy/Ozempic, they rapidly regain weight. (Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism: Journal, June 2022) Experts say this is because the drug is not a cure and it does not prevent the metabolic adaptation that occurs during weight loss. A study published in April 2022 which sought to examine changes in body weight and cardiometabolic risk factors upon the termination of the drug, found that after a year people had regained two-thirds of the weight they had lost. The positive changes they had seen in cardiometabolic risk factors like blood pressure, blood lipids, HbA1c, and C-reactive protein had similarly reversed.According to the study authors, these findings reinforce the need to continue treatment in order to maintain the benefits of the medication. (Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism: Journal, April 2022) The fact that people may need to stay on Wegovy indefinitely in order to maintain the weight loss has raised concerns about long-term use. (NPR, 2023) As a nutrition coach, I have been asked several times about these two drugs. I always suggest talking with your doctor about this and making sure that this is the right answer for you. My opinion though is to always work on lifestyle, diet and fitness interventions first. I would invest in a coach before I spent the money on this very expensive drug. If you have further questions, shoot me a DM, we’ll talk. EVERYBODY IS TALKING ABOUT IT. Unless you follow Dr. Oz, the #ketowarriors, or the descendants of Vegan Gains — you’ve heard that a “calorie deficit” is the key to losing fat. We’ll get into details later, but to refresh: a “calorie deficit” simply means your body is burning more calories than you’re consuming (i.e., calories out > calories in = weight loss (few exceptions)). A “calorie surplus” means you’re burning fewer calories than you’re consuming (i.e., calories out < calories in = weight gain). And if you’re eating at your “maintenance calories,” you’re burning around the same number of calories as you’re consuming (i.e., calories out = calories in = maintain stable weight). Now, I could get deep into the minutia of calories in calories out and how your body “burns” calories, but you probably don’t care about the science. What you do care about: me knowing the science and giving you the actionable steps to put into practice. And that’s exactly what I’m gonna do, so take a quick glance at this pretty picture and let’s keep it movin’. That’s the why. Now, I’ll share the how.
For the record, I’ve never seen another fitness coach put this information out for free. This is exactly how I set up a calorie deficit for my online coaching clients, so listen up. STEP 1: BUY SCALES. Buy a bodyweight scale and a food scale. These are reasonably cheap and some of the best investments you can make for managing your body. Plus, there are two things humans suck at: estimating and remembering data. In fact, one study on daily food reporting showed even dietitians to be off by up to 800 calories. Some non-dietitians were off by over 1,000 calories! So, yeah. Buy the scales so you don’t do this. STEP 2: DOWNLOAD A FOOD TRACKING APP. I recommend FatSecret or My Fittness Pal to my clients. Don’t use the macro calculator for any of them as that’s the point of this post ⏤ this way is more accurate. MFP might just be more accessible in terms of how to use the app for some people. However, another downside of MFP is their calories can be off with some of their foods due to user inputted data. Just make sure your total daily macros match up to your total daily calories and you’ll be good to go. Any tracking app or using a pad and pen (if you’re a neanderthal) will work just fine. We’ll cover your macros (proteins, carbs, and fats in a bit). STEP 3: EAT NORMALLY AND TRACK EVERYTHING. Without drastically changing how you currently eat, track every single thing (very important this is accurate!) you put in your mouth for at least four days (preferably three weekdays and one weekend day). I say to eat normal because you want to find your current baseline. If you go changing everything you eat, you’ll skew your results. And when I say track everything, I mean EVERYTHING — alcohol, condiments, oils, drinks, supplements, butter, sauces, dessert, etc. STEP 4: AVERAGE OUT YOUR BASELINE. After tracking at least four days, find the average number of calories you ate during that time period. For example:
STEP 5: REMAIN CONSISTENT WITH TRACKING WEIGHT AND FOOD FOR 14 DAYS.Try to hit within +/- 50 of that average calorie amount (2,150 – 2,250) every single day for the next 2 weeks (including weekends!) AND weigh yourself every day in the morning – before you eat and after you take your morning dump. It’s important you try to mimic each day so you can get a realistic idea of what your “typical” intake and weight would look like, i.e., don’t do this during vacation. STEP 6: ANALYZE WEIGHT TRENDS. Given that you followed step 5 correctly, we should now see a trend in what your weight does based off how much food you’re eating. If you’re eating ~2,200 calories per day and your weight is trending downward (not down every single day because weight fluctuates) over the course of two weeks — you’re likely in a calorie deficit. If your weight is staying about the same (within a pound or so), subtract 250 calories from your daily calorie goal and keep consistent. This means you are eating around your maintenance calories. If your weight is trending upward, take away 350-500 calories per day (you’re in a calorie surplus). -Coach Kayli  I want to teach you where you should put the majority of your focus on if you're wanting to lose fat, build some muscle and just care about your overall health. This Hierarchy was explained very well to me by my Coach Jeremiah Bair. I would love to share with you what I have learned from him. To the right, you will see The Fitness Hierarchy Ranked from most-least important:
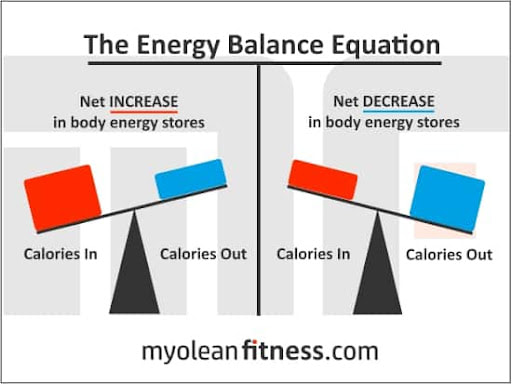
Most people are surprised by this, expecting cardio to be the number one focus, followed by stepping into the gym a few times, and dieting hard for a couple weeks every January. Now why doesn’t this work? Nutrition In order to lose fat we must eat fewer calories than we burn in a day. It is impossible to erase a poor diet with exercise. Why? Because you just don’t burn very many calories when you exercise (about 5% of your total daily calorie burn comes from exercise.) Calories in < Calories out = Fat Loss. This is called Energy Balance Main takeaway here is watching your diet to control the “calories in” side of the energy balance equation is much easier than trying to lose fat by ramping up the “calories out” side of the equation. This is why Nutrition is the most important factor to pay attention to. Resistance Training Lifting weights actually burns fewer calories than cardio. But, resistance training has many more benefits for you than cardio:
It’s rewarding It’s a huge psychological boost Find a plan you can see yourself sticking to for a really long time. Cardio Cardio is still helpful. We just don’t want to put the majority of our focus in it. Cardio has obvious cardiovascular health benefits-it’s good for your heart. Cardio has carryover to your resistance training. It allows you to recover quicker - both between sets and between training sessions. Now the biggest issue with cardio is that your body adapts very quickly to it. When you adapt to something, you become more efficient at it. Becoming efficient means you’re burning less calories. So take this for example: If you were to run 1 mile you might burn 100 calories. As the adaptation occurs, the calorie burn decreases. So after running a mile every day this week and burning a 100 calories each time you may end up only burning 90 calories the next week, and then 80 the next. The only way to keep burning 100 calories is to increase the distance and/or time spent running. The problem is - who has the time or desire in our busy lives to keep adding miles forever? Conclusion:
-Coach Kayli Questions? Email me: [email protected] Have you ever gone to your doctor asking about ways to lose weight, and the first thing they tell you is that they have a “magic” pill that will help you lose weight fast? All you have to do is take this pill and eat 1,200 calories a day.
Does this sound familiar to you? Unfortunately, this seems to be common practice. Did you know that on average, U.S. medical schools only offer on average 2.8 hours of instruction on obesity, nutrition and physical activity counseling. That sure doesn’t seem like much time dedicated to nutrition to me, but then again, this isn’t normally why we see our family doctors. They are great at many other things but sustainable fat loss isn’t one of them. I have been training and coaching for almost 5 years now and I have had many clients seek my help after having gone through extreme dieting and pills prescribed by their doctor. They dropped a lot of weight fast, but then gained it all back and then some after stopping the pills! For 99% of people, 1,200 calories is way too little to be consuming. Our bodies need that much energy intake just for basic needs, things like breathing and to operate our internal organs. Our bodies are extremely capable of adapting though. This is what has kept us alive for so long. We have survived countless famines throughout history. We used to be hunters/gatherers and only ate when we made a kill or forged and found food. There would be a feast followed by many days of not eating while searching for more food. How did we survive??? We survived because of our bodies ability to adapt. Our metabolisms would “learn” how to run off lower calories and would “slow” down our metabolisms. Meaning we could survive off less food and when we did find food again it would store it as body fat in case of emergencies when there would be no food. Nowadays we rarely have a problem finding food, in fact, we have the complete opposite problem. You can find something to eat on every street corner! We are constantly tempted. Okay, back to why eating 1,200 calories is “wrecking” your metabolism. As described above, our bodies don’t understand that you want to look better in the mirror or drop a couple pant sizes. Your body only knows it isn't receiving enough nutrition to survive long term. So it does its job and lowers your metabolism to keep you alive! I’d say a thanks is in order haha. So rather quickly after eating only 1,200 calories you will notice you are no longer losing weight like you were in the beginning. At first it just slows, then weight loss all together stops. You’ll notice other signs too: constant hunger, cravings, moodiness, poor sleep, skin issues, and women can lose their cycle. This is our body's way of saying, “Hey! I need some nutrition, damn it!” So most of us cave. We go back to eating just like we were before and gain every single pound back. We have to find something sustainable to lose weight, because we will have to continue it to keep that weight off. Enough of the negative. Now, let me share some ways I help my clients lose body fat and keep it off! First, we want to do as little as possible to elicit the most amount of change. Stay with me here. I want my clients to keep eating as much as possible during their fat loss phase. During the first week, we will figure out what their maintenance calories are (what they need to eat to stay at their current weight.) Once we find this number, we will lower their intake by just 250-500 calories max. You will start to see fat loss from this amount. A sustainable fat loss rate is around 1-2 pounds per week. If you are losing more than 2 pounds per week you are not eating enough to keep your metabolism in a healthy place. After a few weeks, their calories may need to be lowered again to keep seeing results but this is why we start high so we have room to make adjustments along the way. Next, I will have them incorporate resistance training 1-2 days per week. Resistance training is proven to build and preserve muscle on our bodies. The more muscle we have on our bodies, the more calories our bodies will burn at rest. It will keep our metabolism “higher.” Plus, I believe you may find yourself to look more aesthetically pleasing with the added muscle. Last, and definitely not the least. . . We program in periodization. This simply means we don’t want to stay in this fat loss phase for longer than 8-24 weeks depending on their size and how much fat they want/need to lose. There needs to be times where you go back to eating at maintenance again or even in a surplus to get your body back to a healthier place. Yes, you may put a few pounds back on but if done properly, it won't be much. If you try to rush the process and stay in a fat loss phase for a long amount of time you will end up “slowing” down your metabolism and end up gaining all the weight you just lost and sometimes more! If you still have weight to lose, you can always go back into a fat loss phase after spending some time in a maintenance phase. The key takeaways here are:
I hope this helps you in your fat loss journey and if you would like even more guidance, I have a few spots opening up soon in my online coaching. Shoot me a DM and let’s talk about what you are struggling with the most right now and see if I can help. |
AuthorKayli is a certified personal trainer and online coach that specializes in fitness, wellness, nutrition, mindset, mobility and everything in between. Categories
All
Archives
June 2024
|
Call Us 620-757-9146
Home | About Us | Personal Training | Online Nutrition and Fitness Coaching | Custom Training Plans | Breakfast | Entrees | Dressings | Snacks | Blog
Phoenix Rising Podcast | Product Recommendations | Contact Me
Phoenix Rising Podcast | Product Recommendations | Contact Me
Copyright 2024 Kayli Montoya Fitness